Timing things
As can be read in Scenes aka Levels, there are two different
implementations of YaegerScene available: a StaticScene and a
DynamicScene. Their main difference resides in the fact that a DynamicScene
contains a Game World Update (GWU) to which all instances of DynamicEntity
added to the scene will listen.
This chapter will discuss the different ways in the GWU can be used within Yaeger. It will start by discussing how the GWU gets delegated to all objects, after which different ways to use in within your scene of entity.
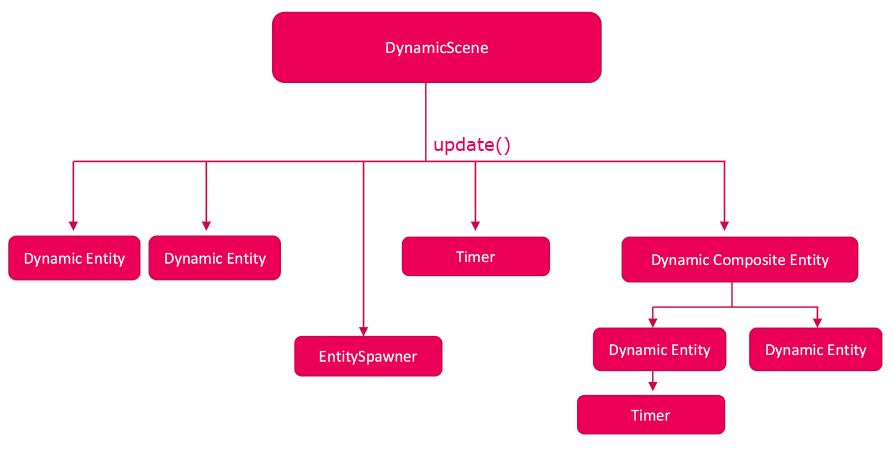
How the GWU is delegated to all objects
The GWU is initiated by the DynamicScene, and handed down to all dynamic
entities that were added to the scene. This is done in the same order as in
which they were added to the scene.
Pausing and resuming the GWU
Since the GWU gets initiated at the level of the DynamicScene, and then
passed down, it is possible to pause all objects that are called by this
GWU. For this a DynamicScene provides a method to pause and resume the GWU.
Using a Timer to create time-based events
On both dynamic scenes and dynamic entities one or more timers can be used
to create time based events. To use such a Timer the scene or entity
should implement the interface TimerContainer. After doing so, the method
setupTimers() should be implemented and the method addTimer(Timer) can
be called to add an instance of Timer.
Exposing the GWU to scenes and entities
The GWU is kept internal on all entities and scenes and gets delegated
downwards. It is, however, possible to expose the GWU to an entity or scene by
implementing the interface UpdateExposer, which exposes an explicitUpdate (long) method. The value passed to this method represents a timestamp
of the current time and can be used to keep track of time.